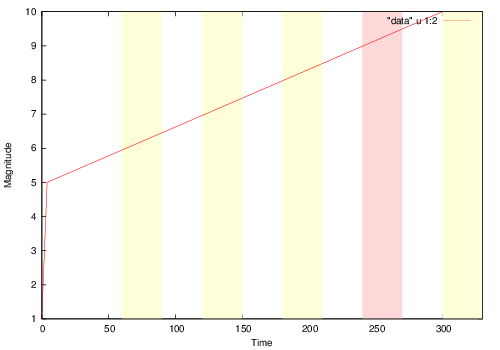
Marking intervals in gnuplot graph (with shading)
I needed to mark intervals on a gnuplot line plot different colors. Critically, I didn’t want to have to set the y start and end points (as you would if just drawing a rectangle). Turns out you can do this in gnuplot with a rect object and it’ll figure it out, such that it covers the graph area.
Example code is below (the “data” data file should contain x y datapoints 1 set per line in this example):
set terminal postscript eps color set output "data.eps" set xlabel "Time" set ylabel "Magnitude" set xrange [0:330] set style rect fc lt -1 fs solid 0.15 noborder set obj rect from 240, graph 0 to 270, graph 1 fc rgbcolor "red" set obj rect from 360, graph 0 to 390, graph 1 fc rgbcolor "red" set obj rect from 420, graph 0 to 450, graph 1 fc rgbcolor "red" set obj rect from 540, graph 0 to 570, graph 1 fc rgbcolor "red" set obj rect from 720, graph 0 to 750, graph 1 fc rgbcolor "red" set style rect fc rgbcolor "yellow" set obj rect from 60, graph 0 to 90, graph 1 set obj rect from 120, graph 0 to 150, graph 1 set obj rect from 180, graph 0 to 210, graph 1 set obj rect from 300, graph 0 to 330, graph 1 plot "data" u 1:2 with lines